Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
What are the top 10 medications for anxiety and depression? With millions of adults worldwide navigating these conditions, finding safe, effective treatment is critical. This comprehensive guide explores the top 10 clinically proven medications prescribed for anxiety and depression, backed by the latest research and expert guidelines. From widely used SSRIs like Prozac to fast-acting benzodiazepines and beta-blockers, we break down how these treatments work, their benefits, potential side effects, and key considerations to help you or your loved ones make informed decisions about mental health care.
Understanding Anxiety and Depression

Anxiety and depression are interconnected mental health disorders that often coexist. Globally, 5% of adults experience depression, while anxiety disorders impact 40 million U.S. adults yearly. Anxiety triggers excessive worry about future threats, while depression manifests as persistent sadness, fatigue, and loss of interest. Both can disrupt daily life, but evidence-based treatments—including medication—offer significant relief.
Top 10 Medications for Anxiety and Depression

Below are the most commonly prescribed medications, grouped by class and highlighted for their efficacy in managing symptoms.
1. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Examples: Prozac (fluoxetine), Zoloft (sertraline), Lexapro (escitalopram)
How They Work: Boost serotonin levels, improving mood and reducing anxiety.
Efficacy: First-line treatment for both conditions; 70–80% of patients see symptom improvement.
Side Effects: Nausea, insomnia, sexual dysfunction.
Key Fact: May take 4–6 weeks to take full effect.
2. Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
Examples: Effexor (venlafaxine), Cymbalta (duloxetine), Pristiq (desvenlafaxine)
How They Work: Increase serotonin and norepinephrine, enhancing emotional regulation.
Efficacy: Effective for severe depression and chronic pain-related anxiety.
Side Effects: Increased blood pressure, sweating, insomnia.
3. Benzodiazepines
Examples: Xanax (alprazolam), Valium (diazepam), Ativan (lorazepam)
How They Work: Enhance GABA activity for rapid anxiety relief (30–60 minutes).
Efficacy: Ideal for short-term panic attacks or acute anxiety.
Risks: High addiction potential; not recommended for long-term use.
4. Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
Examples: Elavil (amitriptyline), Tofranil (imipramine)
How They Work: Block serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake.
Efficacy: Reserved for treatment-resistant cases due to side effects.
Side Effects: Dry mouth, constipation, dizziness.
5. Beta-Blockers
Examples: Inderal (propranolol), Tenormin (atenolol)
How They Work: Reduce physical anxiety symptoms (e.g., rapid heartbeat).
Efficacy: Often used for performance anxiety or situational stress.
6. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
Examples: Nardil (phenelzine), Marplan (isocarboxazid)
How They Work: Increase serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine by blocking MAO enzymes.
Efficacy: Effective but rarely prescribed due to dietary restrictions and side effects.
7. Atypical Antidepressants
Examples: Wellbutrin (bupropion), Remeron (mirtazapine)
How They Work: Target dopamine or norepinephrine instead of serotonin.
Efficacy: Useful for patients with SSRI intolerance or weight/appetite concerns.
8. Antipsychotics (Adjunctive Therapy)
Examples: Abilify (aripiprazole), Seroquel (quetiapine)
How They Work: Boost the effect of antidepressants in treatment-resistant cases.
Efficacy: FDA-approved for major depressive disorder (MDD) augmentation.
9. Buspirone
How It Works: A non-benzodiazepine anxiolytic targeting serotonin receptors.
Efficacy: Low-risk option for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
10. Esketamine (Spravato)
How It Works: NMDA receptor antagonist administered via nasal spray.
Efficacy: Fast-acting for treatment-resistant depression; requires clinical supervision.
Beyond Medication: Holistic Treatment Options
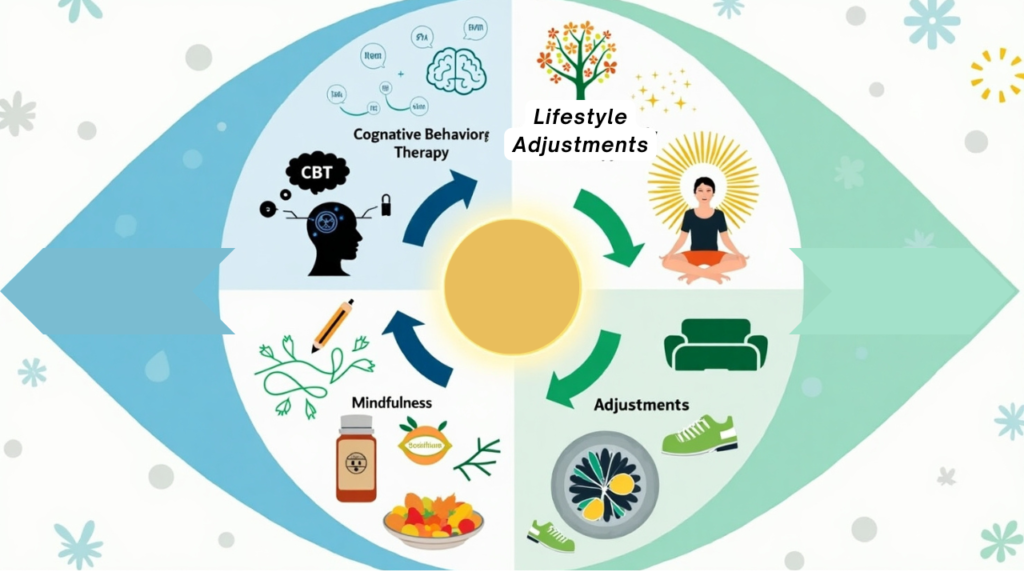
While medications are pivotal, combining them with therapy enhances outcomes:
-
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Reshapes negative thought patterns.
-
Mindfulness & Meditation: Reduces stress and improves emotional resilience.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments: Regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and sleep hygiene.
Diagnosis and When to Seek Help
A doctor diagnoses anxiety or depression through:
Symptom Assessment: Questionnaires like the PHQ-9 or GAD-7.
Medical History Review: Rule out thyroid issues or vitamin deficiencies.
Physical Exam: Check for underlying health conditions.
Seek help if:
Symptoms persist for 2+ weeks.
Daily functioning is impaired.
Suicidal thoughts emerge.
Key Takeaways

SSRIs/SNRIs: First-line treatments with balanced efficacy and tolerability.
Benzodiazepines: Short-term relief for acute anxiety.
Combination Therapies: Medication + CBT often yields the best results.
Always consult a healthcare provider to tailor treatment to your needs. What works for one person may not suit another—personalized care is essential.
By understanding these options, you can take proactive steps toward mental wellness. Share this guide to empower others navigating anxiety and depression!
🌱💙
For more mental health insights, visit TheHealthCore.com.
Note: This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice. Always consult a licensed healthcare provider before starting or stopping medication.

