If you take vitamins, you may wonder: What is the best time to take vitamins for optimal absorption? The answer depends on the type of vitamin, whether it’s water-soluble or fat-soluble, and how it interacts with food and other supplements. While some vitamins can be taken at any time, others work best with meals or on an empty stomach. Proper timing can enhance nutrient absorption, prevent side effects, and maximize their benefits.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the best time to take vitamins, including B vitamins, vitamin C, vitamin D, iron, magnesium, and omega-3s. We’ll also explore how food, medications, and lifestyle habits affect absorption, along with practical tips to create an effective supplement routine.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Water-Soluble vs. Fat-Soluble Vitamins

Vitamins fall into two main categories, which determine how they’re absorbed and stored:
- Water-Soluble Vitamins
These nutrients readily mix with water and pass through the body quickly, requiring regular replenishment since excess amounts exit through urine.
- Examples:B-complex vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12) and vitamin C.
- Best taken:Any time of day, with or without food (though some may cause stomach upset if taken alone).
- Fat-Soluble Vitamins
These nutrients depend on dietary fats for proper uptake and accumulate in the body’s fatty tissues and liver for later use.
- Examples:Vitamins A, D, E, and K.
- Best taken:With a meal containing healthy fats (avocado, nuts, olive oil, or fatty fish).
Best Time to Take Water-Soluble Vitamins
B Vitamins (Energy & Metabolism Support)
B vitamins (like B12, folate, and B6) help convert food into energy, support brain function, and reduce fatigue.
• Optimal Timing:
o Can be taken any time of day, but many prefer mornings since they aid energy metabolism.
o Taking them with food reduces nausea (especially B6 and niacin).
o Vitamin B12 (especially for deficiencies) shows better uptake when taken before meals, but a small meal is fine if needed.
• Special Cases:
o Pregnant women often take folate (B9) in the morning to combat nausea.
o Older adults may absorb B12 better via sublingual (under-the-tongue) forms.
Vitamin C (Immunity & Collagen Support)
Vitamin C supports immunity, skin health, and iron absorption.
• Optimal Timing:
o Can be taken morning or night, but splitting doses (e.g., 500 mg twice daily) may improve absorption.
o If taking high doses (1,000+ mg), take with food to avoid stomach upset or diarrhea.
o Pair with iron (if supplementing) to enhance absorption—take both with orange juice for better results.
Best Time to Take Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Vitamin D (Bone & Immune Health)
Vitamin D is crucial for calcium absorption, immunity, and mood regulation.
- Optimal Timing:
- Take with the largest meal of the day(dinner is ideal) since fat improves absorption by 30–50%.
- Avoid taking with caffeine(coffee/tea), which may reduce absorption.
- Best paired with vitamin K2(helps direct calcium to bones, not arteries).
Vitamin A, E, and K (Antioxidants & Blood Health)
- Vitamin A (Vision & Immunity):Take with a fat-containing meal (e.g., eggs or avocado).
- Vitamin E (Skin & Antioxidant):Best absorbed with nuts or seeds.
- Vitamin K (Blood Clotting & Bones):Take with dinner alongside vitamin D for synergy.
Caution: High doses of fat-soluble vitamins can be toxic—stick to recommended amounts unless supervised by a doctor.
Best Time to Take Key Minerals
Iron (Energy & Oxygen Transport)
Iron deficiency is common, especially in women and vegetarians.
- Optimal Timing:
- Before meals(1 hour before or 2 hours after) for optimal uptake.
- If stomach irritation occurs, take with vitamin C-rich foods(bell peppers, citrus).
- Avoid:Dairy, coffee, tea, calcium, or antacids within 2 hours (they block absorption).
Magnesium (Muscle Relaxation & Sleep)
Magnesium aids sleep, muscle recovery, and stress reduction.
- Optimal Timing:
- At bedtime(especially magnesium glycinate) to promote relaxation.
- With foodif taking magnesium citrate (can cause loose stools on an empty stomach).
- Avoid high doses with calcium(they compete for absorption).
Zinc (Immunity & Wound Healing)
- Take between meals(if tolerated), or with a light meal.
Avoid with iron or copper supplements (they interfere with absorption).
Omega-3s (Heart & Brain Health)

Fish oil (EPA/DHA) reduces inflammation and supports cognitive function.
- Optimal Timing:
- With meals(fat improves absorption and reduces fishy aftertaste).
- Split doses(morning and night) if taking high amounts (e.g., 2,000+ mg).
Factors That Affect Vitamin Absorption
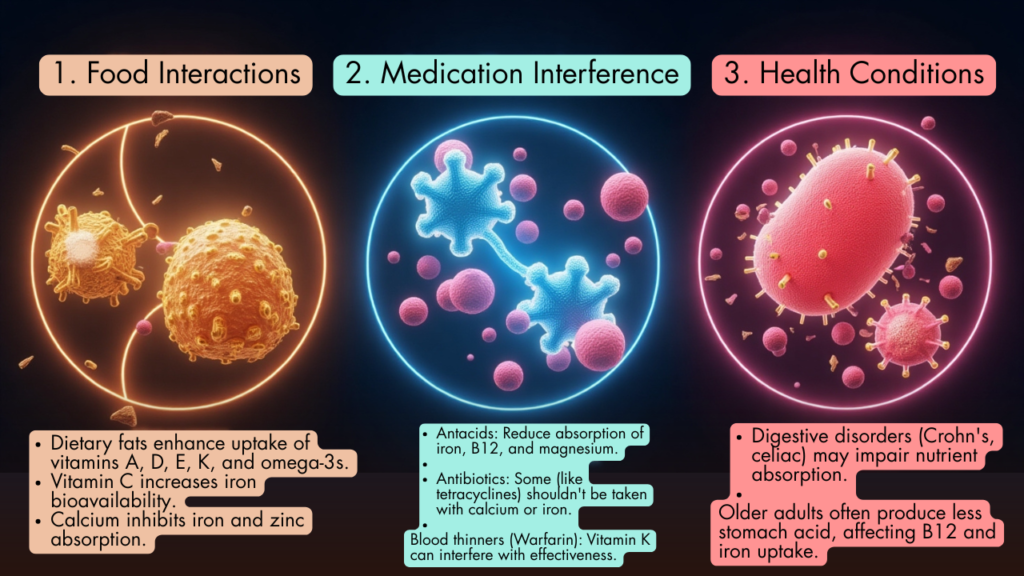
- Food Interactions
- Dietary fats enhanceuptake of vitamins A, D, E, K, and omega-3s.
- Vitamin C increasesiron bioavailability.
- Calcium inhibitsiron and zinc absorption.
- Medication Interference
- Antacids:Reduce absorption of iron, B12, and magnesium.
- Antibiotics:Some (like tetracyclines) shouldn’t be taken with calcium or iron.
- Blood thinners (Warfarin):Vitamin K can interfere with effectiveness.
- Health Conditions
- Digestive disorders(Crohn’s, celiac) may impair nutrient absorption.
- Older adultsoften produce less stomach acid, affecting B12 and iron uptake.
Sample Daily Vitamin Schedule
Time | Supplement | Notes |
Morning | B-complex, Vitamin C | With breakfast (light meal). |
Lunch | Iron (if needed) | With orange juice (no dairy). |
Dinner | Vitamin D, K2, Omega-3s | Take with fatty fish or avocado. |
Before Bed | Magnesium Glycinate | Aids sleep and muscle recovery. |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Consuming iron with coffee/tea(tannins block absorption).
- Exceeding recommended doses of fat-soluble vitamins(risk of toxicity).
- Combining calcium and iron(take them 4+ hours apart).
- Taking fat-soluble vitamins without dietary fats(reduces absorption by 50%).
FAQ: Your Vitamin Timing Questions Answered
- Is it okay to take all supplements together?
Water-soluble vitamins (B, C) can be combined, but minerals like iron, zinc, and calcium should be spaced out to prevent competition for absorption.
- What should I do if I forget a dose?
Take the missed dose when you remember, but skip it if your next scheduled dose is approaching. Avoid taking extra to compensate.
- When should I take vitamins relative to exercise?
- Before workout:B vitamins for energy support.
- After workout:Magnesium for muscle recovery.
- Are gummy vitamins equally effective?
They often contain lower nutrient levels and added sugars—check labels for complete formulations.
Key Takeaways

The ideal timing for vitamin supplementation varies by nutrient type:
- Water-soluble (B, C):Flexible timing, with food if needed.
- Fat-soluble (A, D, E, K):Always combine with fat-rich meals.
- Iron/Zinc:Ideally between meals for maximum uptake.
- Magnesium:Evening administration promotes relaxation.
- Omega-3s:Pair with meals containing fats.
Pro Tip: Use a weekly pill organizer and set reminders to maintain consistency. For personalized guidance, consult a healthcare professional—particularly if managing deficiencies or medications.
By strategically timing your vitamin intake, you’ll optimize nutrient absorption, minimize side effects, and enhance your supplement regimen’s effectiveness!

