Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues, including arthritis, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders. Fortunately, certain supplements can help combat inflammation effectively. If you’re on the hunt for best anti-inflammatory supplements to calm inflammation, you’ve landed in the ideal spot. This guide explores the top natural options to reduce inflammation and promote overall wellness.
Table of Contents
ToggleTop 10 Best Anti-inflammatory Supplements
1. Turmeric (Curcumin)
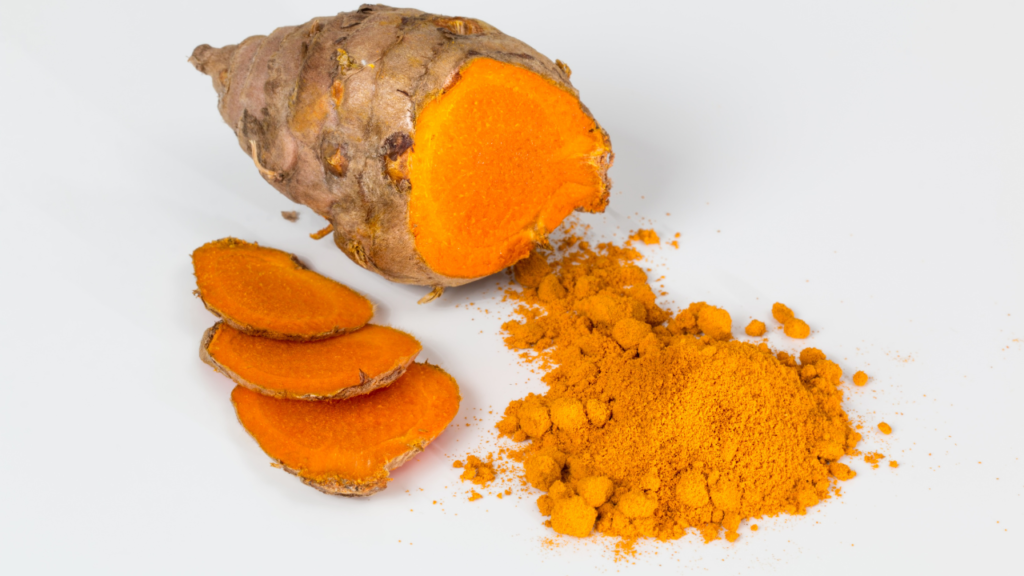

Turmeric, specifically its active compound curcumin, is one of the best anti-inflammatory supplements available. Studies show that curcumin can reduce inflammation as effectively as some pharmaceutical drugs, without the side effects. It works by blocking inflammatory pathways in the body, making it beneficial for conditions like arthritis and metabolic syndrome.
For better absorption, pair turmeric with black pepper (piperine) or take it in liposomal form. A standard intake usually falls between 500 and 2,000 mg daily.
2. Omega-3 Fatty Acids (Fish Oil)
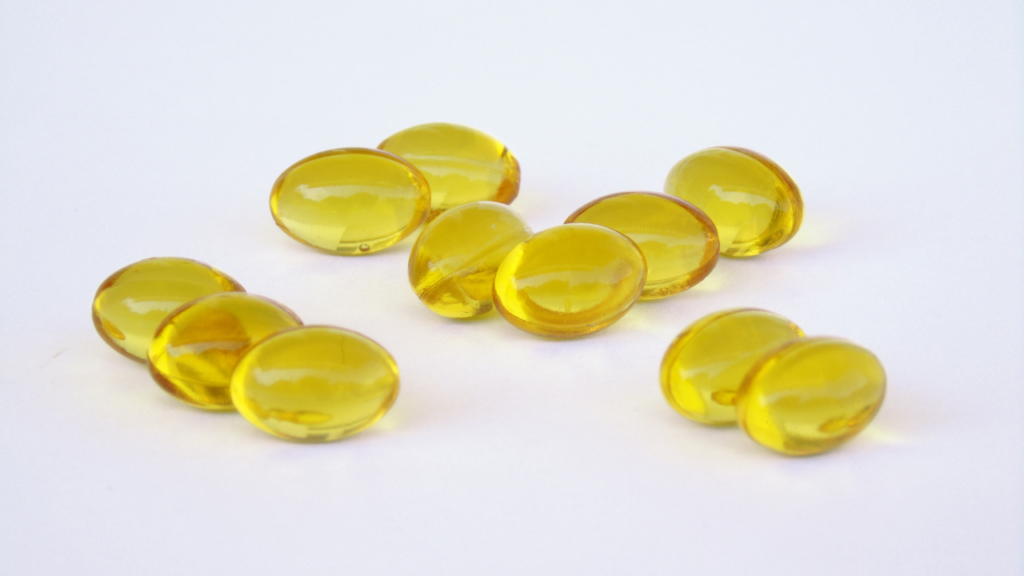

Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, are powerful inflammation fighters. They help lower the production of inflammatory molecules like cytokines and eicosanoids. Research suggests that omega-3s can reduce symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, heart disease, and even depression.
The best sources include fatty fish (salmon, mackerel) or high-quality fish oil supplements. Aim for 1,000–3,000 mg daily of combined EPA and DHA for optimal benefits.
3. Ginger Extract
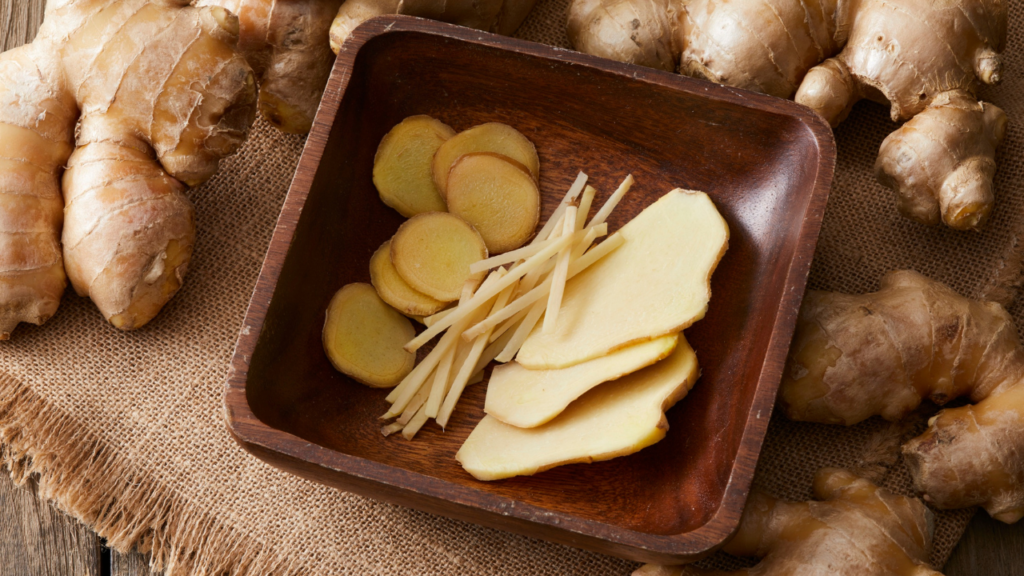

Ginger is rich in gingerol—a potent natural substance known for its soothing and antioxidant effects. It’s particularly effective in reducing muscle pain, osteoarthritis discomfort, and digestive inflammation.
You can consume ginger as a tea, in fresh form, or as a supplement (1,000–2,000 mg daily). Its warming effect also aids digestion, making it a dual-purpose supplement.
4. Resveratrol

Found in red wine, grapes, and berries, resveratrol is a potent antioxidant that combats inflammation at the cellular level. It activates sirtuins, proteins linked to longevity and reduced inflammation. Studies indicate it may protect against heart disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders.
A typical dose ranges from 150–500 mg per day, though higher amounts may be used under medical supervision.
5. Bromelain
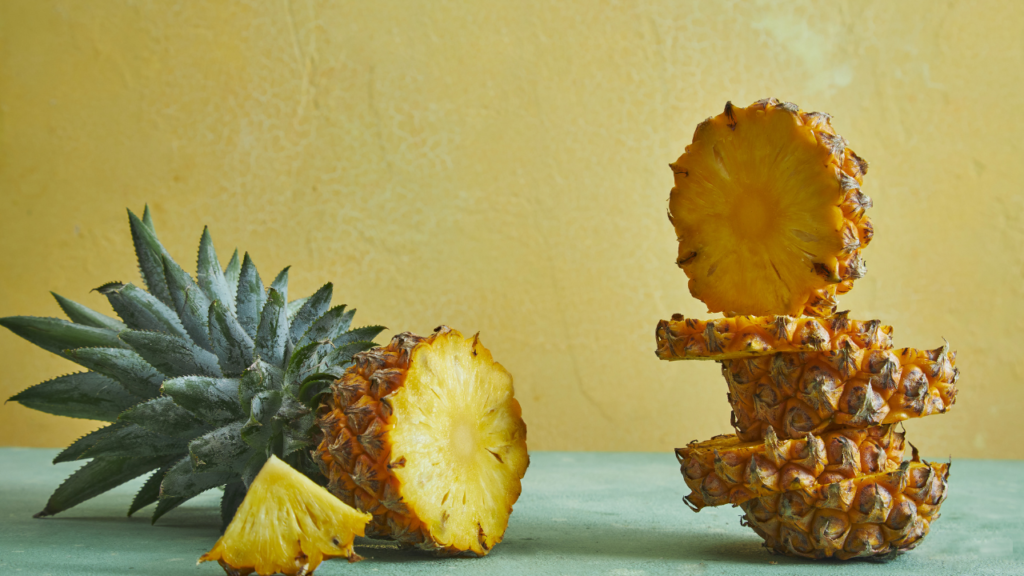

Derived from pineapples, bromelain is an enzyme that reduces swelling, improves digestion, and speeds up recovery from injuries. It’s especially useful for post-surgery inflammation and sinusitis.
For anti-inflammatory effects, take 500–2,000 mg daily between meals.
6. Green Tea Extract (EGCG)
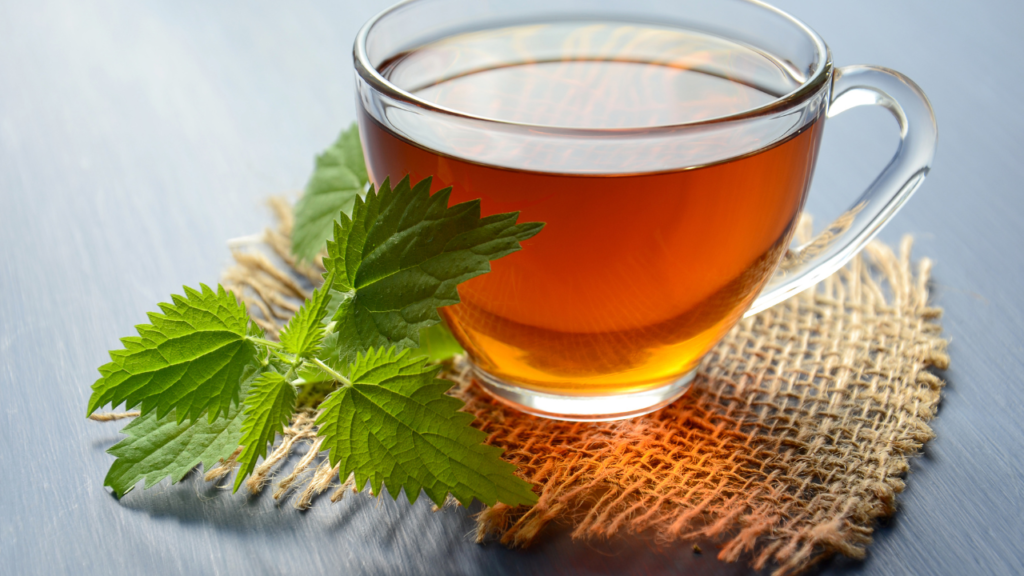

Green tea is rich in epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a compound that suppresses inflammation and oxidative stress. It’s particularly beneficial for metabolic health and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Drinking 2–3 cups of green tea daily or taking 300–500 mg of EGCG extract can provide significant benefits.
7. Vitamin D
Deficient vitamin D levels have been associated with heightened inflammatory responses. This essential vitamin modulates the immune system, reducing excessive inflammatory responses. Many people are deficient, especially in winter, making supplementation crucial.
A daily dose of 1,000–5,000 IU is generally safe, but testing your levels is ideal for personalized dosing.
8. Boswellia Serrata
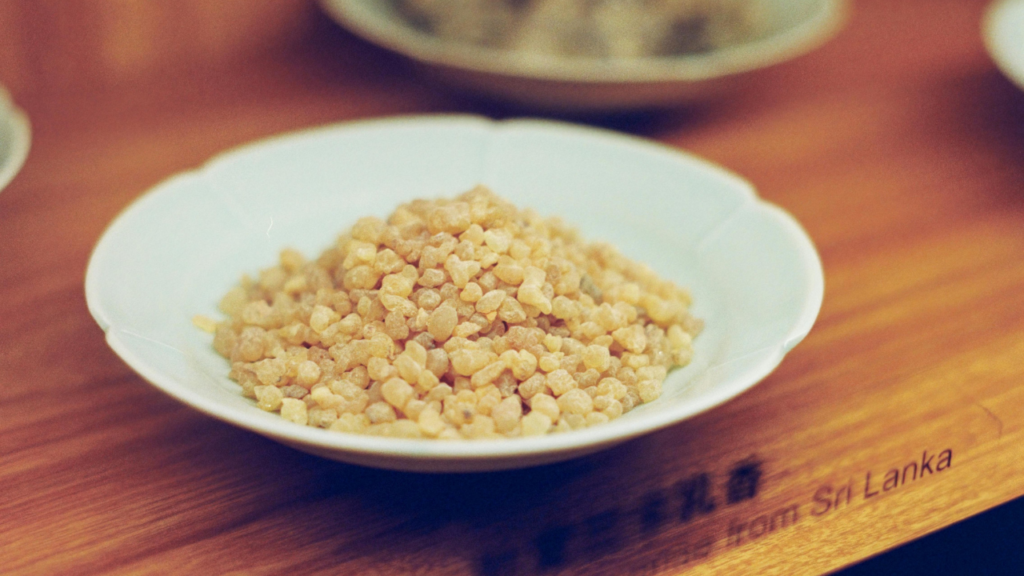

Also known as Indian frankincense, Boswellia contains acids that block pro-inflammatory enzymes. It’s highly effective for joint pain, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and asthma.
A standard dose is 300–500 mg taken 2–3 times daily.
9. Quercetin

A flavonoid found in apples, onions, and berries, quercetin stabilizes mast cells, which release histamine during allergic reactions. It’s excellent for reducing allergy-related inflammation and supporting cardiovascular health.
Supplement with 500–1,000 mg per day for best results.
10. Probiotics
Gut health directly impacts inflammation. Probiotics balance gut bacteria, reducing systemic inflammation linked to obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune diseases. Probiotic strains such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium offer notable anti-inflammatory benefits.
Aim for 10–30 billion CFUs daily from a high-quality probiotic.
Final Thoughts on the Best Anti-Inflammatory Supplements

Chronic inflammation is a silent contributor to many diseases, but incorporating the best anti-inflammatory supplements can help manage it naturally. Turmeric, omega-3s, ginger, and other powerful compounds provide science-backed benefits without harsh side effects.
Before starting any new supplement, consult a healthcare provider, especially if you’re on medication. Pair these supplements with an anti-inflammatory diet (rich in leafy greens, berries, and healthy fats) for maximum results.
By choosing the best anti-inflammatory supplements, you take a proactive step toward better health, reduced pain, and enhanced longevity. Start with one or two options, monitor your body’s response, and adjust as needed for optimal wellness.

